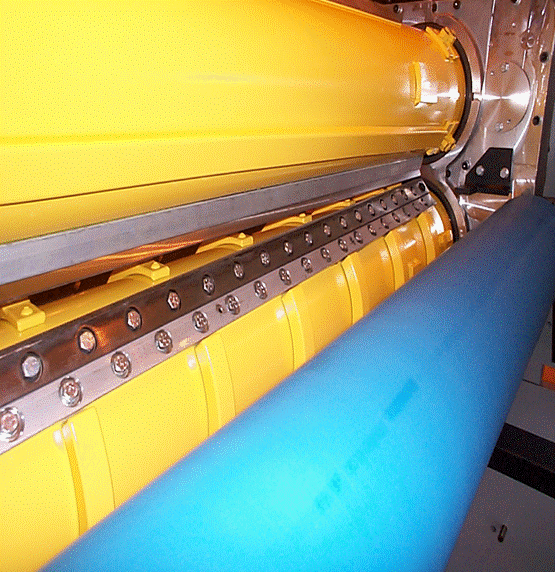
Technological Advancements in Blade Design
Evolution of Cutting Technology…
With the use of advanced technology, the journey from simple straight blades of yester-year to today’s advanced helical designs, represents decades of engineering innovation in cardboard production:
- Historical Perspective:
- Early manual cutting methods
- Introduction of mechanised straight blades
- Development of rotary die-cutting
- Revolution of CNC-controlled helical blades
- Metallurgical Innovations:
- High-speed steel (HSS) compositions
- Tungsten carbide coating technologies
- Nano-structured blade materials
- Custom alloys for specific applications
Blade Geometry Optimisation
The science behind blade design goes far beyond simple sharpness:
- Cutting Angle Analysis:
- Impact of rake angle on cut quality
- Clearance angle optimisation
- Edge preparation techniques
- Micro-geometry considerations
- Computer-Aided Design:
- Finite Element Analysis for stress distribution
- Computational Fluid Dynamics for dust-management
- Thermal analysis for high-speed operation
- Vibration modeling for stability
Advanced Control Systems Architecture
Multi-Layer Control Structure
Modern CNC systems employ sophisticated control architectures:
- Real-Time Control Layer:
- Microsecond-level response times
- Dedicated motion control processors
- Real-time operating systems (RTOS)
- Deterministic communication protocols
- Supervisory Control Layer:
- Production recipe management
- Operator interface systems
- Historical data collection
- Integration with MES systems
Adaptive Control Strategies
Intelligent adaptation to changing conditions:
- Dynamic Parameter Adjustment:
- Real-time cutting speed optimisation
- Automatic feed rate adjustment
- Adaptive acceleration control
- Load-based parameter tuning
- Learning Algorithms:
- Pattern recognition for material variations
- Statistical modeling of performance data
- Neural networks for predictive control
- Fuzzy logic for complex decision-making
Maintenance and Reliability Engineering
Predictive Maintenance Strategies
Keeping CNC cutters operating at peak performance:
- Condition Monitoring Technologies:
- Vibration analysis systems
- Acoustic emission sensors
- Thermal imaging for bearing health
- Motor current signature analysis
- Data-Driven Maintenance Planning:
- Machine learning for failure prediction
- Remaining useful life estimation
- Optimal maintenance scheduling
- Spare parts inventory optimisation
Reliability-Centered Maintenance
Ensuring maximum uptime and performance:
- Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA):
- Critical component identification
- Risk priority number calculation
- Mitigation strategy development
- Continuous improvement processes
- Performance Monitoring:
- Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE) tracking
- Six Sigma methodologies application
- Statistical Process Control (SPC)
- Root cause analysis protocols
Safety Systems and Operator Protection
Integrated Safety Features
Modern CNC cutters prioritise operator safety:
- Physical Safeguards:
- Light curtains and safety scanners
- Interlocked guard systems
- Emergency stop systems
- Safe speed monitoring
- Software Safety Systems:
- Safety-rated motion control
- Dual-channel safety circuits
- Safe Torque Off (STO) functionality
- Safety PLC integration
Safety Standards Compliance
Meeting and exceeding industry safety requirements:
- Regulatory Frameworks:
- ISO 13849 compliance
- CE marking requirements
- OSHA standards adherence
- Industry-specific safety guidelines
- Safety Assessment and Validation:
- Risk assessment methodologies
- Safety function validation
- Regular safety audits
- Operator safety training programs
Industry 4.0 Integration and Digital Twins
Digital Twin Technology
Creating virtual representations of physical systems:
- Real-Time Simulation:
- Physics-based modeling of cutting processes
- Virtual commissioning capabilities
- Performance optimisation through simulation
- Operator training applications
- Predictive Analytics:
- What-if scenario analysis
- Production optimisation modeling
- Virtual sensor implementation
- Anomaly detection and prediction
Advanced Connectivity
Enabling seamless integration with smart factory systems:
- Communication Protocols:
- OPC UA implementation
- MQTT for lightweight data transfer
- Time-Sensitive Networking (TSN)
- 5G industrial wireless connectivity
- Data Management:
- Edge computing implementation
- Cloud integration for data storage
- Real-time data visualisation
- Cybersecurity measures
Future Trends and Emerging Technologies
Next-Generation Cutting Systems
Looking ahead to future innovations:
- Advanced Materials:
- Self-sharpening blade materials
- Nano-engineered cutting surfaces
- Smart materials for adaptive performance
- Eco-friendly material developments
- Quantum Computing Applications:
- Complex optimisation algorithms
- Advanced simulation capabilities
- Real-time pattern recognition
- Predictive maintenance enhancement
Sustainable Technologies
Pushing the boundaries of eco-friendly production:
- Energy Innovation:
- Zero-emission cutting systems
- Energy harvesting technologies
- Sustainable power management
- Carbon footprint reduction strategies
- Circular Economy Integration:
- Closed-loop material recycling
- Biodegradable cutting fluids
- Remanufacturing of components
- Life cycle assessment tools
Customer Success Stories and Case Studies
Implementation Experiences
Real-world examples of successful CNC cutter deployments:
- Large-Scale Operations:
- Challenges faced and overcome
- ROI achievement timelines
- Production efficiency improvements
- Quality enhancement results
- Specialty Applications:
- Unique customer requirements
- Customisation success stories
- Innovation driven by customer needs
- Market advantage achievements
Shaping the Future of Packaging
As we’ve explored throughout this comprehensive guide, CNC cutters with helical blades represent far more than just a technological advancement in corrugated cardboard production – they embody the convergence of precision engineering, digital innovation, and sustainable manufacturing practices.
From the microscopic details of blade geometry to the macroscopic view of industry-wide digital transformation. Every aspect of these remarkable machines has been optimised for performance, reliability, and efficiency. As we look to the future, the continued evolution of CNC-cutting advanced technology promises even greater achievements in speed, precision, and sustainability.
Advanced Material Handling Systems
A critical component often overlooked in discussions about CNC cutters is the sophisticated material handling systems that supports these high-speed operations. Let’s explore how these systems work in tandem with cutting corrugated cardboard production technology.
Automated Feed Systems
Modern corrugator lines employ advanced feed systems that ensure consistent material flow to and from the CNC cutters:
- Vacuum Belt Technology: High-powered vacuum belts grip and transport sheets without marking or damaging the cardboard surface.
- Dynamic Tensioning: Intelligent tensioning systems automatically adjust to maintain optimal material tension, crucial for accurate cutting.
- Multi-Zone Control: The feed path is divided into multiple independently controlled zones, allowing for precise speed matching and gap control.
Stacking and Palletising
After cutting, equally important is how the finished sheets are handled:
- High-Speed Stackers:
- Can handle up to 200 sheets per minute
- Use air jets and mechanical stops for precise alignment
- Equipped with automatic reject systems for defective sheets
- Robotic Palletising:
- Vision systems ensure perfect stack placement
- Multiple pallet patterns can be programmed
- Real-time adjustment for varying sheet sizes
Quality Control and Monitoring Systems
In-Line Inspection Systems
Modern CNC cutting lines incorporate sophisticated quality control measures:
- Optical Measurement Systems:
- High-speed cameras capture images of every cut
- AI-powered image analysis detects deviations in real-time
- Capability to measure within 0.1mm accuracy
- Surface Quality Monitoring:
- Checks for crush marks or damage from handling
- Monitors score depth and consistency
- Verifies print registration when applicable
Data Collection and Analysis
The integration of Industry 4.0 principles has revolutionised quality control:
- Statistical Process Control (SPC):
- Real-time data collection from multiple sensors
- Trend analysis for predictive quality control
- Automatic adjustment of cutting parameters
- Digital Quality Records:
- Complete traceability for every batch produced
- Automated quality reports-generation
- Integration with customer quality systems
Environmental Considerations and Sustainability
Energy Efficiency Innovations
Modern CNC cutting systems are designed with sustainability in mind:
- Energy Recovery Systems:
- Regenerative braking in servo motors
- Heat recovery from hydraulic systems
- Smart standby modes during production gaps
- Waste Reduction Technologies:
- Optimised nesting algorithms minimise offcuts
- Trim collection and recycling systems
- Digital prototyping reduces material waste during setup
Eco-Friendly Practices
The corrugated industry is embracing green technologies:
- Water-Based Hydraulic Systems:
- Replacing traditional oil-based systems
- Reduced environmental impact in case of leaks
- Improved safety for operators
- Sustainable Maintenance Practices:
- Biodegradable cleaning solutions
- Recyclable blade materials
- Extended service intervals through predictive maintenance
Economic Impact and ROI
Investment Considerations
When evaluating CNC cutting systems, several factors impact ROI:
- Initial Investment vs. Long-term Benefits:
- Higher initial cost compared to traditional cutters
- Significantly lower per-unit production costs
- Typical ROI period of 1-3 years for high-volume operations
- Operational Cost Savings:
- Reduced labour costs through automation
- Lower maintenance costs due to predictive systems
- Energy savings from efficient motors and systems
Productivity Improvements
The economic benefits extend beyond direct cost savings:
- Increased Market Competitiveness:
- Faster turnaround times for customer orders
- Ability to handle more complex cutting patterns
- Higher quality output leading to premium pricing
- Flexibility and Scalability:
- Quick changeover between different product sizes
- Easy integration of additional capacity
- Ability to handle rush orders without disrupting scheduled production
Training and Operator Expertise
Skill Requirements
Modern CNC cutting systems require a new breed of operator:
- Technical Competencies:
- Understanding of G-code, Basic++, python etc, programming
- Basic troubleshooting skills
- Knowledge of quality control systems
- Digital Literacy:
- Ability to interact with HMI interfaces
- Understanding of production management software
- Basic data analysis skills
Training Programs
Companies are investing in comprehensive training:
- Virtual Reality Training Simulators:
- Safe environment for operator training
- Realistic simulation of various scenarios
- Performance tracking and assessment
- Ongoing Education:
- Regular updates on new features and capabilities
- Cross-training for operational flexibility
- Certification programs for operators
Customisation and Special Applications
Industry-Specific Adaptations
CNC cutting systems are often customised for specific industries:
- Retail Packaging:
- High-speed production of retail-ready packaging
- Integration with digital printing systems
- Special coatings and finishes
- Industrial Packaging:
- Heavy-duty cutting capabilities
- Specialised blade designs for thick materials
- Enhanced durability for continuous operation
Specialty Products
Advanced CNC systems enable unique applications:
- Point-of-Purchase Displays:
- Complex cuts for intricate designs
- Multi-level cutting for 3D structures
- Scoring patterns for easy assembly
- Protective Packaging:
- Customised cushioning designs
- Integration with foam-in-place systems
- Optimised for shipping efficiency
Conclusion:
The Cutting Edge of Innovation
As we’ve explored in this comprehensive overview, CNC cutters with helical blades are far more than just cutting tools – they’re the cornerstone of modern corrugated cardboard production. From advanced material handling and quality control to sustainability and economic considerations, these systems represent the pinnacle of manufacturing technology.
As the industry continues to evolve, we can expect even more innovations in this field. The future of corrugated packaging is being shaped by these precise, powerful, and intelligent machines, driven by the never-ending quest for better quality, higher efficiency, and more sustainable production methods.
For manufacturers, converters, and end-users alike, understanding and embracing these advancements is not just about staying competitive – it’s about being part of a technological revolution that is reshaping the packaging industry. As we move forward, the lessons learned, and innovations developed in CNC cutting technology will undoubtedly continue to influence and inspire developments across the entire manufacturing sector.
Whether you’re a seasoned industry professional or just starting to explore the world of corrugated packaging, understanding the capabilities and impact of CNC cutting technology is crucial. It’s not just about cutting cardboard – it’s about cutting a path to the future of packaging manufacturing across the board!